Introduction:
Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy (BPBP) is a condition that affects newborns, causing weakness or paralysis in the arm due to damage to the brachial plexus nerves. This condition can be distressing for parents and may raise numerous questions.
In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy, providing patients and their families with a better understanding of this condition.
What is the Brachial Plexus?
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves arising from spinal cord in the neck and going to the upper limb. It is formed by contributions from five nerve roots called C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1.
It supplies motor power to the muscles of the shoulder, elbow, wrist and hand, and also sensations to the skin of the upper limb.
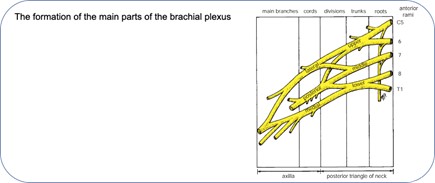
What is the Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy (BPBP)?
Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy (BPBP) is a condition in which the brachial plexus gets damaged during child-birth due to stretching of the child’s neck during passage through the birth canal. It results in paralysis of muscles of the shoulder/ elbow/ wrist/ hand and loss of sensations in the upper limb.

What are the types of BPBP?
Depending on the number of nerve roots damaged, Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy is of following types:
Type 1: C5 and C6 nerve roots damaged. Results in weakness of shoulder and elbow flexion. Wrist and finger movements are intact.
Type 2: C5, C6 and C7 nerve roots damaged. Results in weakness of elbow and wrist extension in addition to the weakness seen in Type 1.
Type 3: All nerve roots from C5 to T1 resulting in flail upper limb.
Type 4: In addition to Type 3, drooping of eyelid (Horner’s syndrome) seen due to damage to surrounding nerves. May also be associated with elevation of hemi-diaphragm and breathing difficulties due to phrenic nerve palsy.
Usually, Type 1 injuries have a good prognosis for spontaneous recovery. On the other hand, Type 3 and Type 4 injuries have no chance for recovery unless surgery if performed.
Depending on the severity of injury, nerve injury in Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy is classified as:
Neuropraxia: Stretching of the nerve without actual tear. Results in temporary paralysis which spontaneously recovers in few days.
Axonotmesis: rupture of axons (inner nerve fibers) but outer covering nerve sheaths remain intact. Usually recover partially, as the nerve fibers regrow within the sheaths over a period of few weeks.
Neurotmesis: Complete breakage of nerves. Surgical repair mandatory for recovery.
Root avulsions: Nerves are avulsed at their origin from the spinal cord. Direct repair not possible, nerves supplying other muscles need to be transferred for recovery.

What are the causes of Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy?
The primary cause of BPBP is trauma during delivery, which can occur in the following situations:
Shoulder Dystocia: This happens when the baby’s shoulder gets lodged behind the mother’s pelvic bone during delivery.
Macrosomia: When a baby is significantly larger than average, the risk of shoulder dystocia and brachial plexus injury increases.
Breech Presentation: If the baby is positioned feet-first instead of head-first during delivery, there is an increased likelihood of brachial plexus injury.
What are the signs and symptoms of Brachial Plexus Birth Palsy?
- Decreased movements of the upper limb are usually noted soon after birth.
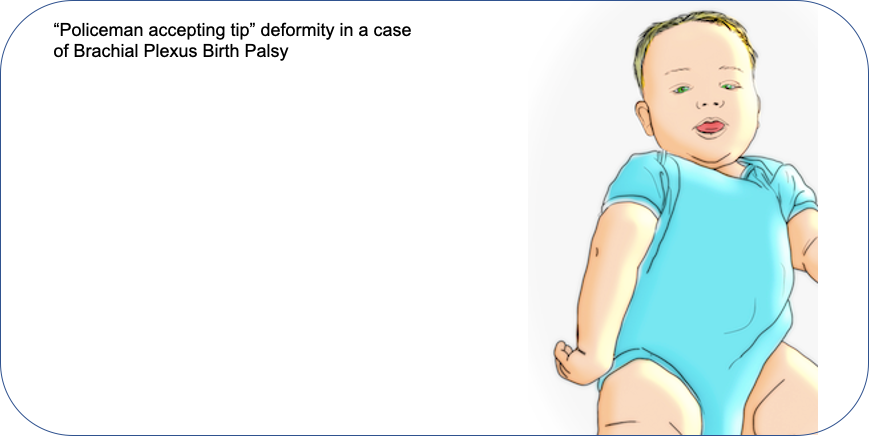
- In upper plexus palsy (Type 1), the baby holds the upper limb in the typical “Policeman accepting tip” position with shoulder adducted and internally rotated, elbow extended, forearm pronated and wrist flexed.
- In global plexus palsy (Types 3 and 4), the upper limb is flail without any movements.
- There may be associated fractures of clavicle or humerus.
1- As the child grows older, the paralysis may recover to a variable extent depending on the severity of injury and treatment.
2- Older children with partial recovery often have shoulder joint problems with deformity of the shoulder joint due to muscle imbalance, difficuly in performing overhead abduction, and difficulty in bringing the hand to the mouth for feeding.
3- Additionally, deformities of the elbow and wrist may be seen.
Investigations:
1- X-rays: Plain X-rays done soon after birth may reveal associated fractures of the clavicle and humerus, and, elevation of the hemi-diaphragm.
2- MRI:
• MRI of brachial plexus may be done prior to nerve reconstructive surgery and aids in surgical planning.
• MRI shoulder done in older children with shoulder joint problems shows shoulder joint deformation.
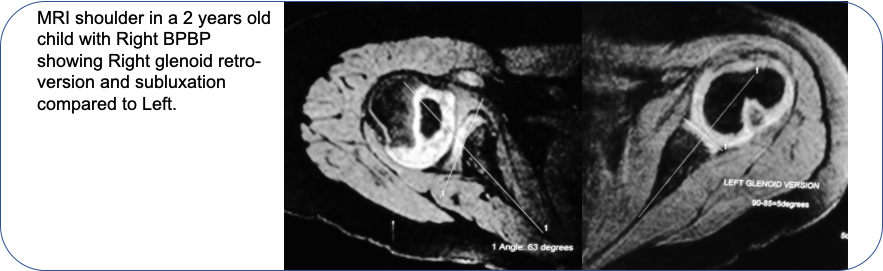
- EMG/NCV studies: show nerve conduction. They are helpful in tracking nerve recovery.
Treatment:
1- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy is instituted about 2 to 3 weeks after birth. The aim of physiotherapy is to range the joints of the upper limb through full range of motion and prevent contractures due to persistent positioning in paralytic posture.
2- Splints and orthoses: Splints and orthoses may be used to maintain the shoulder/ elbow joints in a functional position, and to prevent contractures.
Surgery:
• Nerve reconstructive surgery: Nerve reconstructive surgery is needed in children with flail upper limbs (Type 3 and 4 injuries) and in children in who fail to achieve satisfactory recovery of elbow flexion power between 3 to 6 months age. Nerve reconstructive surgeries are either nerve repairs where nerve grafts are used to repair the damaged nerves or nerve transfers where nerves supplying other muscles are transferred to the paralysed nerve.
• Injection Botox: Injection Botox is given in young children who develop shoulder joint contractures, or in situations called co-contractions where muscle contractions occur in a haphazard manner leading to impaired joint movements.
• Shoulder joint surgery: Shoulder joint surgery is commonly needed in older children who develop shoulder joint contractures and deformities. The surgery may consist of release of tight muscles, transfer of muscles, bony surgeries or combinations of the above.
• Elbow/ wrist/ hand surgery: Occassionally elbow, wrist and hand surgeries are needed to correct muscle imbalance or joint deformities.



0 Comments