Que: 1- What is ‘pulled elbow’?
Ans: ‘Pulled elbow’, also called ‘Nursemaid’s elbow’ is an injury to the elbow that occurs in young children below the age of 4 years.
Que: 2- How does pulled elbow occur?
Ans: Pulled elbow occurs when a sudden pull is applied across the extended elbow in a young child.
Pulled elbow typically occurs when a caregiver holds a child’s hand or wrist and suddenly pulls on it, for example, to prevent the child from falling or to help the child climb a step. It can even happen while playing, when an older child swings the young child around holding just his/her hands (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Pulled elbow occurs when a sudden pull is applied across the extended elbow in a young child.

Que: 3- What exactly happens in pulled elbow?
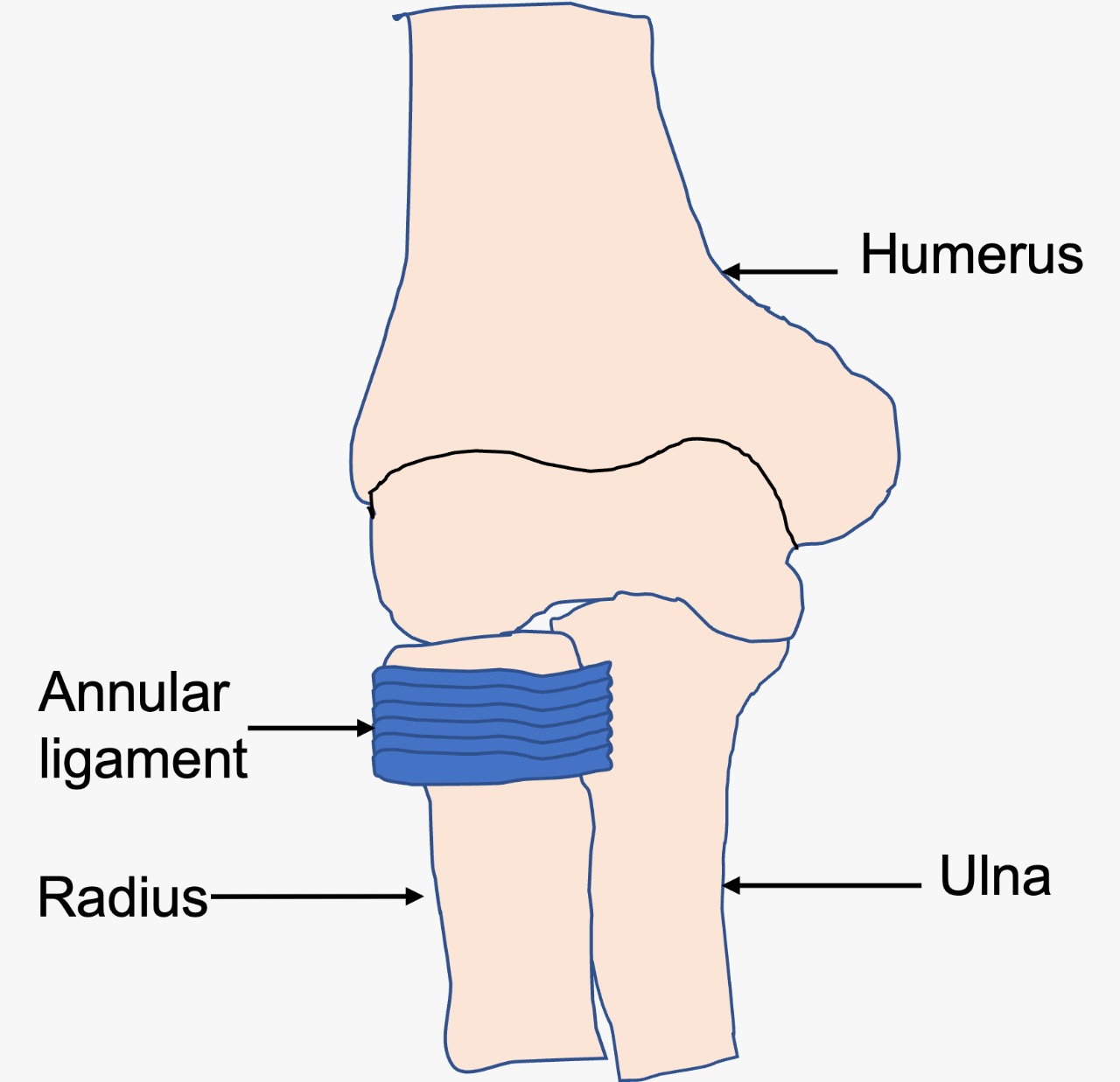
Ans: The elbow joint is formed by articulation between the arm bone (Humerus) and the bones of the forearm (Radius and Ulna). The ‘annular ligament’ is a ligament which is attached to the ulna and encircles the upper end of radius bone called radial head. (Figure 2).
Figure 2: The elbow joint if formed by articulation between the arm bone (humerus) and bones of the forearm (radius and ulna). The annular ligament is attached to the ulna and encircles the radial head.
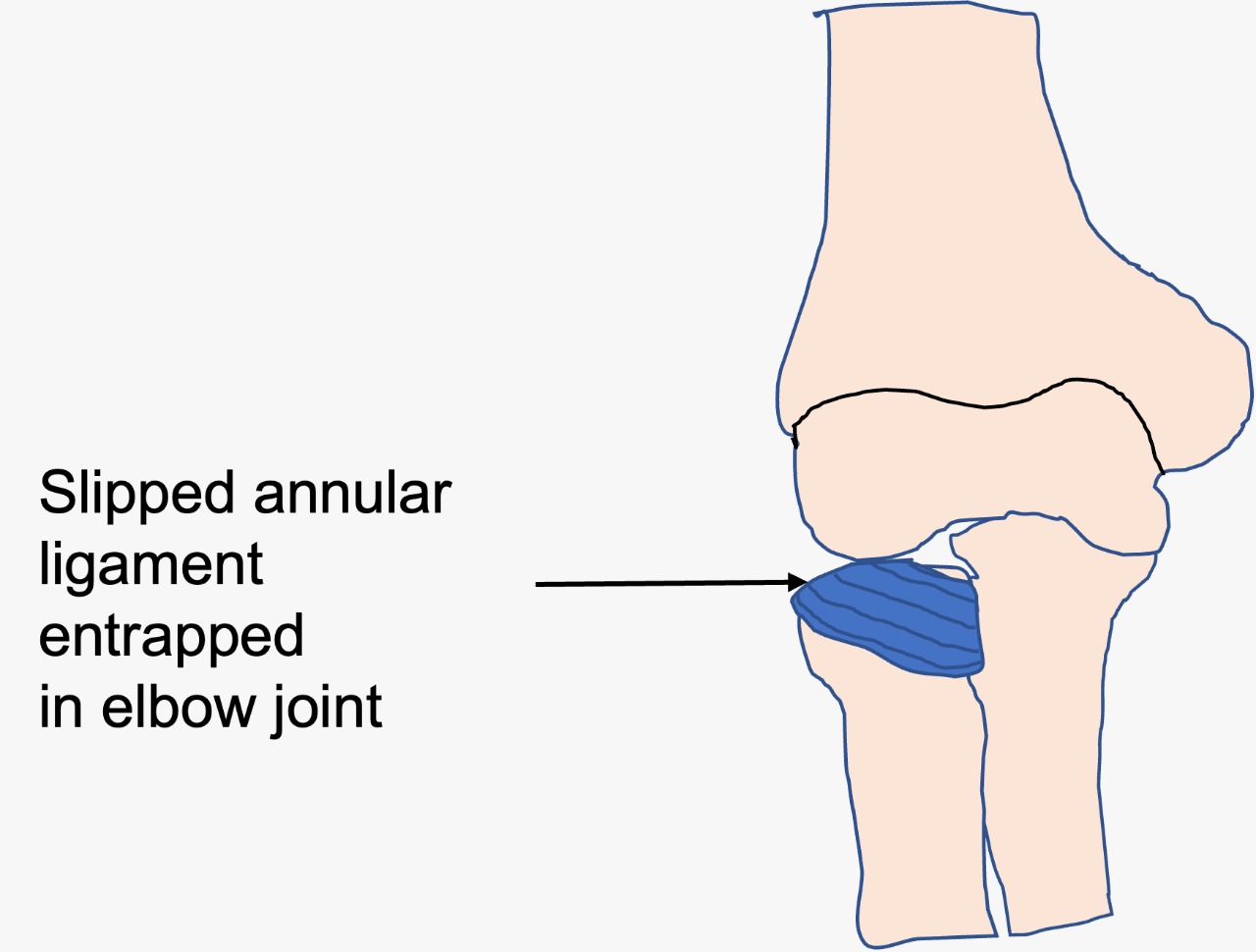
In small children, the annular ligament is a bit loose. When a sudden pull is applied to the child’s elbow, the upper end of radius bone (radial head) can slip from under the annular ligament. This results in pulled elbow (Figure 3).
Figure 3: In small children, the annular ligament is loose. When a sudden pull is applied to the child’s elbow, the radial head can slip from under the annular ligament resulting in pulled elbow.
Que: 4- How does the doctor diagnose pulled elbow?
Ans: There is a typical history of sudden pulling force across the elbow joint. The child cries and refuses to move the entire arm. He/she holds the arm by the side and does not allow anyone to touch it.
Que: 5- Are X-rays required?
Ans: X-rays can be avoided in pulled elbow if the history and clinical examination findings are typical.
However, if there is a history of fall and/or there is significant swelling around the elbow joint, X-rays should be performed to rule out fractures.
Que: 6- How is pulled elbow treated?
Ans: Two types of manoeuvres have been described to reduce pulled elbow:
Hyper-pronation manoeuvre:
1- The examiner places the thumb of one hand on the radial head of the child’s affected elbow.
2- With the other hand, the examiner grasps the child’s hand.
3- The forearm is then hyper-pronated. That is, the forearm is turned so that the palm faces downwards.
4- As the forearm is pronated, usually a click is heard which indicates successful reduction of the pulled elbow (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Hyper-pronation manoeuvre for reducing pulled elbow. The radial head is palpated with thumb of one hand. The child’s hand is grasped with examiner’s other hand and forearm is pronated.

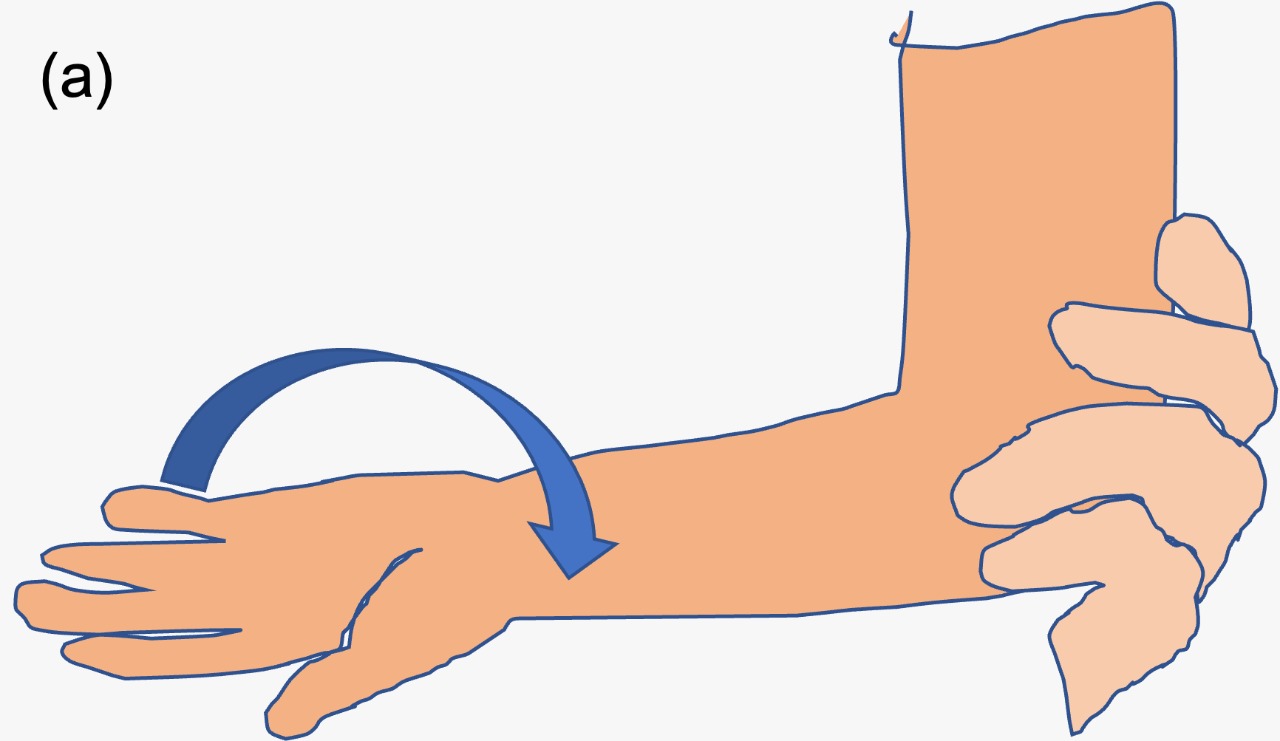
Supination-flexion manoeuvre:
1- The examiner places the thumb of one hand on the radial head of the child’s affected elbow.
2- With the other hand, the examiner grasps the child’s hand.
3- The forearm is then supinated. That is, the forearm is turned so that the palm faces upwards (Figure 5a).
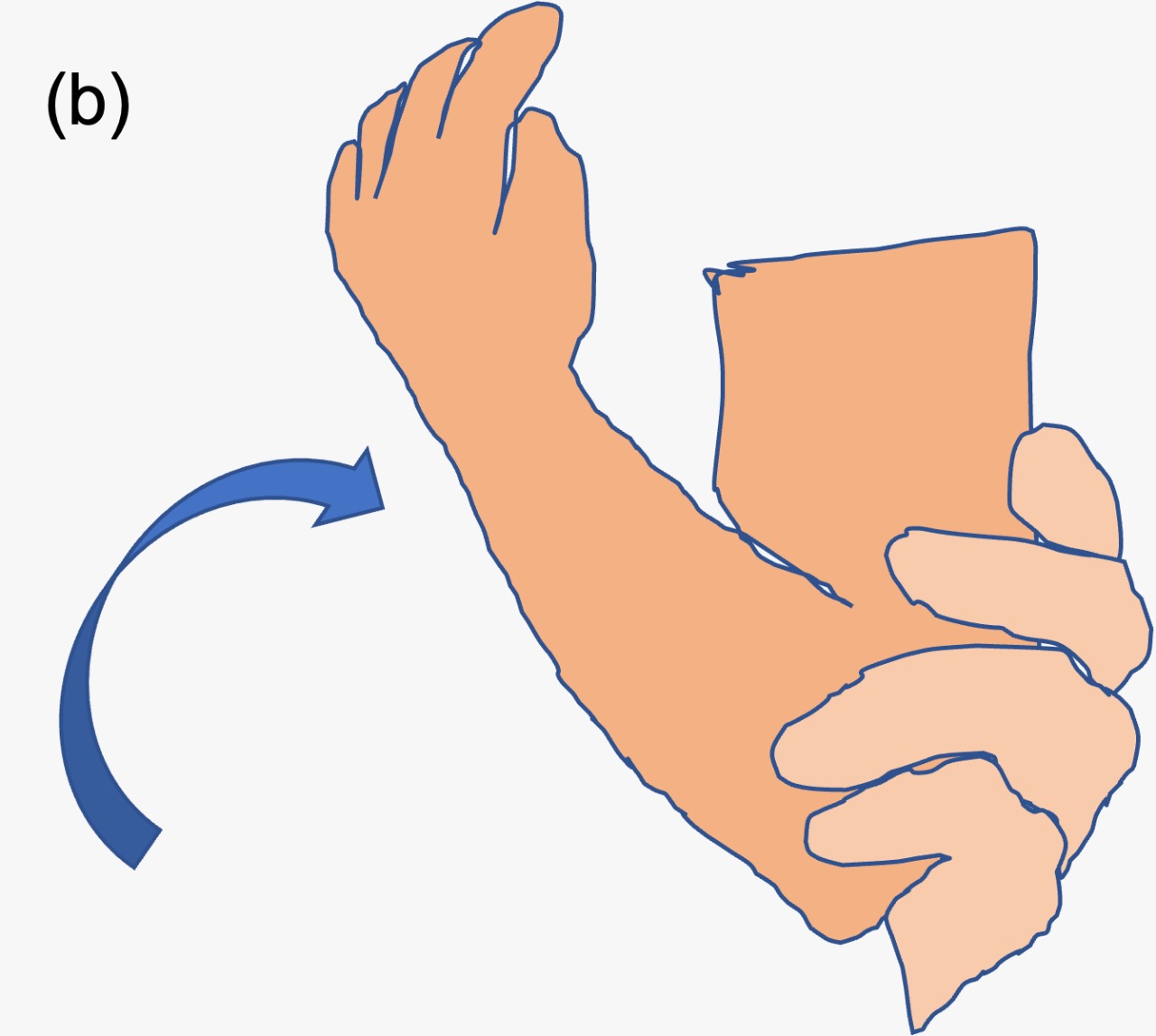
4- The examiner then flexes the elbow to maximal flexion (Figure 5b).
Figure 5: Supination-flexion manoeuvre for reducing pulled elbow. (a) The radial head is palpated with thumb of one hand. The child’s hand is grasped with examiner’s other hand and forearm is supinated. (b) The elbow is then maximally flexed.
Que: 7- How do you know if a pulled elbow has been successfully reduced?
Ans: Successful reduction of a pulled elbow is usually accompanied by a palpable or occasionally audible click. Additionally, the child becomes comfortable and starts active movements of the affected elbow within a short while.
Que: 8- What steps should be taken if reduction of pulled elbow is unsuccessful?
Ans: If first attempt at reducing a pulled elbow fails, one more attempt may be made. However after two unsuccessful attempts, the child’s elbow should be splinted and X-rays/ other investigations should be considered to look for other diagnoses like fractures.
Que: 9- How can recurrent episodes of pulled elbow be prevented?
Ans: It is important to understand that pulled elbow can be recurrent in children under the age of 4 years. To prevent it, parents and caregivers must remember certain simple measures:
1- To safely lift a child, grasp him or her gently under the arms. Do not lift children by holding the hands or arms.
2- Do not swing a child by holding the hands or arms.
3- Avoid tugging or pulling on a child’s hands or arms.
This patient information article is written by Dr Sandeep Vaidya, Division of Children’s Orthopaedics, Pinnacle Orthocentre Hospital. If you have any query, please write in to drsvvaidya@gmail.com. To schedule an appointment, call 7028859555/ (022)25419000/ 25429000.



0 Comments