Introduction
It is very painful condition of hand related to cables (tendons) which are responsible for thumb movement. The location of pain is along the base of thumb at wrist level. It is more commonly seen in dominant hand. Usually there is no obvious history of trauma or injury to get this problem.
What is the problem?
Fig. 1: Location of pain
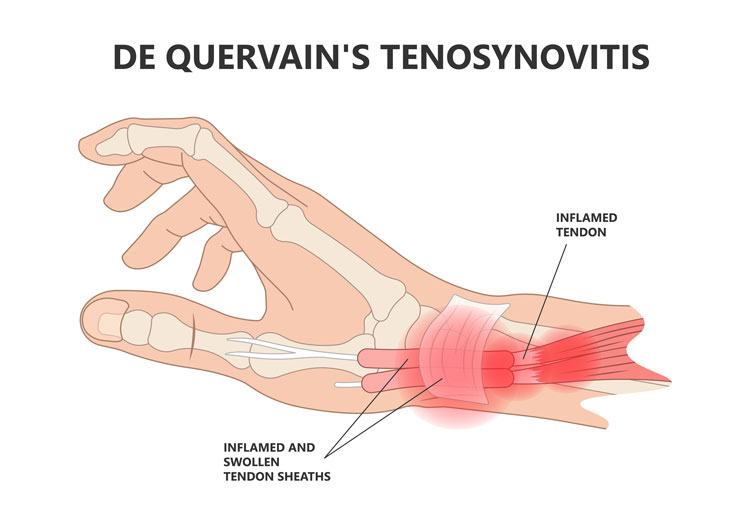
The tendons which are responsible for thumb movements have a sheath at wrist level which wraps the tendons around bone. In de Quervain’s tenovaginitis, the sheath is thickened and obstructs the free gliding of thumb tendons which eventually produces severe pain.
Mainly actions like shaking hand with someone, opening jar or bottle, asking for lift or showing thumbs up and squeezing of cloths etc. are very painful.
Who is more affected?
⁃ females during and after pregnancy
⁃ younger generation using mobile phones and laptops continuously ⁃ those who have diabetes, hypertension, thyroid disorder or rheumatoid arthritis
⁃ also seen in labourers or industrial workers who work on vibratory machines.
Is it a serious or non-solvable problem?
Certainly not!! Actually, thumb contributes to more than 50% function of the hand. If usage of thumb gives pain then person does not use the hand to best of his or her capacity which leads major functional disability. It is 100% solvable problem.
Is there any test to prove it?
X-ray:
If there is significant swelling & history of fall or direct trauma, then we may consider X-ray of the wrist to prove bony problems around that region like overgrowth of bone (radial styloiditis or osteophyte) or bone tumour like Giant Cell Tumour of distal radius.
Ultrasonography:
It gives fair idea about confirmation of diagnosis, diameter or thickness of the tendon sheath & location where it gets stuck.
How do we treat it at Pinnacle Orthocentre Hospital?
After detail examination of patient and tests, various treatment options are considered.
If symptoms are not bothering daily activities then thumb splint & therapy in the form of local ultrasound with medical treatment can be considered.
Fig. 2: Thumb spica splint
Steroid injection in the painful area in some selected patients can give relief without much side effects. In some patients, it may relieve symptoms may show recurrence. We have also observed occurrence of harmless white patch on the skin after injection.
Splintage and steroid injection therapy may work de Quervain’s tenovaginitis seen in pregnant females or post pregnancy.
If symptoms affect activities of daily living then ultimately surgery to release the tendon sheath and making thumb tendons gliding free has to be considered.
Surgery is done as day care procedure. It has excellent success rate if done in time. Person can use operated hand after the surgery within a week or ten days’ time. As it is mostly done under local anaesthesia, surgery is very safe.
