Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Treatment
Arthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing pain and stiffness in the joints, impacting daily life and mobility. While it is most prevalent in older adults, arthritis can affect people of all ages.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, types, and treatment options can help manage the condition more effectively.
This blog will provide a comprehensive guide to arthritis and highlight available treatments, including advanced care options at Pinnacle Orthocentre Hospital in Thane.
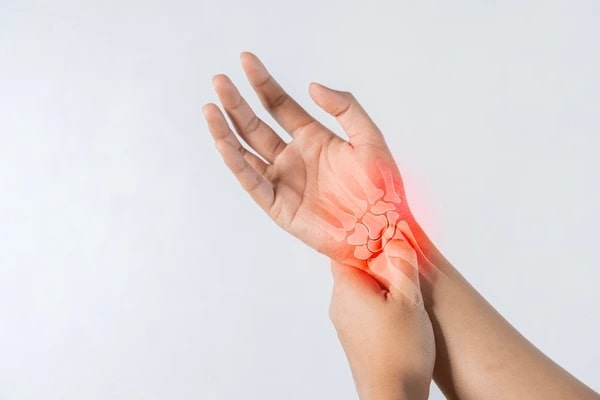
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis refers to inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. The condition affects the joints, causing discomfort that can range from mild to severe.
Prevalence and Impact
Arthritis affects over 350 million people globally, making it one of the leading causes of disability. While there is no cure, early diagnosis and proper treatment can significantly improve quality of life and help maintain joint function.
Arthritis Symptoms
Common Arthritis Symptoms
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type, but the most common signs include:
- Joint pain and tenderness
- Swelling in the joints
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after long periods of inactivity
- Limited range of motion in the affected joints
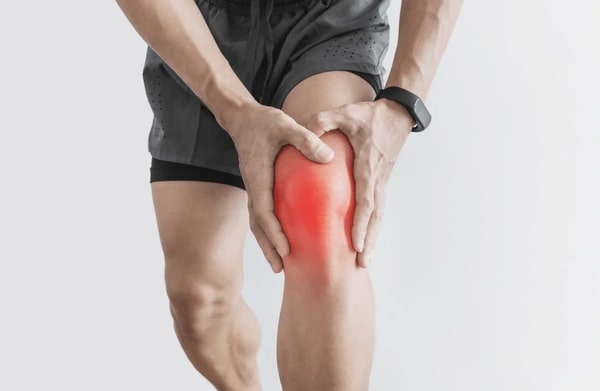
Arthritis in Knee Symptoms
The knees are commonly affected by arthritis, especially osteoarthritis. Symptoms of arthritis in the knee include:
- Pain during movement or while resting
- Swelling and warmth around the knee joint
- Difficulty in walking or climbing stairs
- Stiffness after periods of inactivity
- Signs and Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition that primarily affects the joints. Some common signs of RA include:
- Pain and stiffness in multiple joints (usually symmetrical)
- Swelling and warmth around the joints
- Fatigue, fever, and weight loss as part of systemic symptoms
Arthritis Causes
There are several potential causes of arthritis, depending on the type:
- Wear and Tear (Osteoarthritis): This is the most common type of arthritis, caused by the breakdown of cartilage due to aging, injury, or repetitive joint use.
- Autoimmune Conditions (Rheumatoid Arthritis): RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s joints, causing inflammation and joint damage.
- Infection: Joint infections caused by bacteria or viruses can lead to arthritis, known as septic arthritis.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of arthritis can increase your risk.
- Injury: Past joint injuries can contribute to the development of arthritis, especially osteoarthritis.
Types of Arthritis
There are several types of arthritis, each with different causes and symptoms.
The most common types include:
Osteoarthritis
This is the most common form of arthritis, caused by the breakdown of cartilage in joints. It primarily affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine. Over time, the cartilage deteriorates, leading to pain and stiffness.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
An autoimmune disorder, rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the immune system attacks the synovium (the lining of the joints). This results in inflammation, swelling, and eventual joint damage.
Gout
Gout occurs when uric acid builds up in the bloodstream, leading to the formation of crystals in the joints. It often causes sudden, severe pain, particularly in the big toe.
Psoriatic Arthritis
This type of arthritis affects people with psoriasis, a skin condition. It can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, as well as skin rashes.
Juvenile Arthritis
Juvenile arthritis affects children and adolescents, causing joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, often similar to adult arthritis.
How is Arthritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing arthritis typically involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and blood work.
Physical Examination
During a physical exam, the doctor checks for swollen, tender, or stiff joints, assessing range of motion and symptoms like warmth and redness around the joint.
Diagnostic Imaging
X-rays, MRI, and CT scans may be used to assess the extent of joint damage and inflammation. These tests are particularly useful for diagnosing osteoarthritis and other degenerative joint diseases.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can detect markers of inflammation and specific autoimmune conditions. For example, rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies are common in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Arthritis Treatment Options
What is Arthritis Treatment?
Arthritis treatment aims to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function. The treatment plan may include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery.
Medications
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen and NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can help manage arthritis pain.
Corticosteroids: These drugs help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, especially in autoimmune forms like rheumatoid arthritis.
Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Used to slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis, these medications can help prevent joint damage.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy helps strengthen the muscles around the joints, improve flexibility, and reduce stiffness. Therapists can design exercise programs tailored to specific needs.
Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the pressure on joints, particularly weight-bearing ones like the knees and hips. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, and yoga can also help maintain mobility.
Arthritis Treatment Food
Certain foods can help reduce inflammation and support joint health:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these can help reduce inflammation.
- Antioxidants: Fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants, such as berries, spinach, and broccoli, can help combat inflammation.
- Avoid: Processed foods and high sugar intake, as they can exacerbate inflammation.
Arthritis Surgery in Thane
In severe cases where arthritis pain and stiffness are not managed by medications or therapy, surgery may be recommended. Pinnacle Orthocentre Hospital in Thane offers advanced surgical treatments for arthritis.
Types of Arthritis Surgeries
- Joint Replacement Surgery: This involves replacing the damaged joint with a prosthetic one. Total knee or hip replacements are common procedures for advanced osteoarthritis.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgery used to clean out joint debris or repair damaged cartilage.
- Joint Fusion: For severely damaged joints, fusion surgery may be performed to permanently join two bones, stabilizing the joint.
Recovery from Arthritis Surgery
Recovery after surgery involves physical therapy to restore mobility and strengthen the muscles around the joint. Most patients regain significant pain relief and improved quality of life following surgery.
When to See an Arthritis Pain Treatment Surgeon in Thane
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent joint pain, swelling, or difficulty in performing everyday tasks. If home treatments and medications do not alleviate your symptoms, you may need to consult an arthritis pain treatment surgeon in Thane for advanced treatment options, including surgery.
At Pinnacle Orthocentre Hospital in Thane, you’ll find experienced surgeons who specialize in treating all types of arthritis. The hospital offers personalized treatment plans to help manage your condition and improve joint function.
Conclusion
Arthritis can significantly impact quality of life, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, you can manage the symptoms and prevent further joint damage. Early diagnosis, medications, physical therapy, and surgery are all viable treatment options, depending on the severity of the condition.
Pinnacle Orthocentre Hospital in Thane provides comprehensive arthritis pain treatment to help you regain mobility and live a more active life.


0 Comments