Introduction:
Cerebral palsy (CP) also called “static encephalopathy” affects movement, posture, and muscle coordination. It is caused by damage to the developing brain during pregnancy, childbirth, or shortly after birth. One of the most common orthopaedic issues associated with cerebral palsy is hip problems.
In this article, we will discuss the patho-anatomy, identification and treatment options of hip issues in children with cerebral palsy.
Why do children with cerebral palsy have hip problems?
Cerebral palsy affects the muscles and nerves that control movement and coordination. When these muscles are affected, they may become weak or tight, leading to altered movement patterns and abnormal joint development.
The hips, being a crucial weight-bearing joint, are particularly vulnerable to the effects of cerebral palsy.
1. Spasticity: A common type of cerebral palsy is spastic cerebral palsy, which causes increased muscle tone and stiffness. Spasticity can lead to muscle imbalances around the hips, with hip flexors and adductors being most commonly affected. Due to this, children with cerebral palsy often keep their hips in an attitude of flexion and adduction.
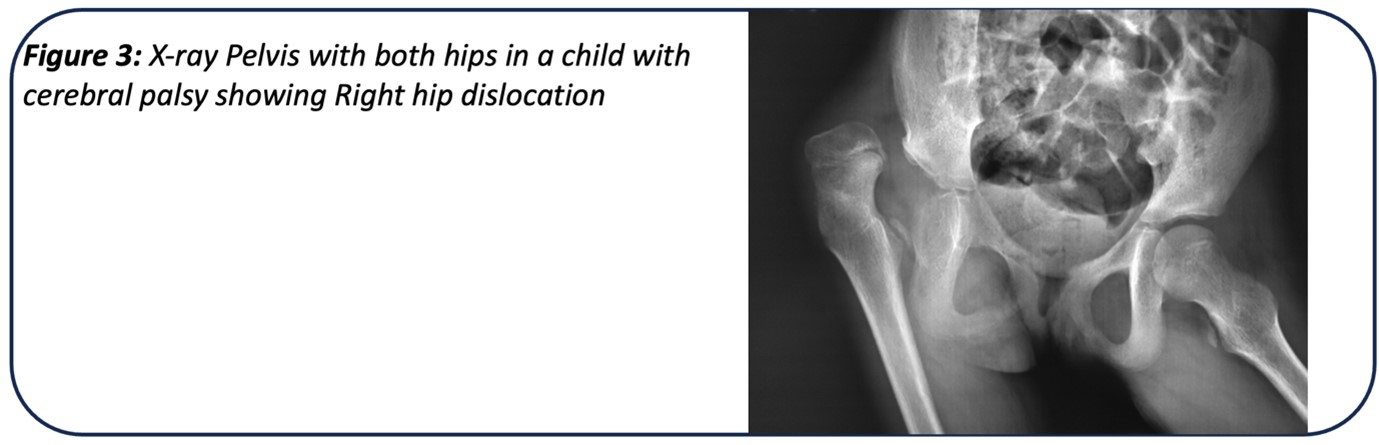
If this spasticity is left untreated, it eventually leads to subluxation and dislocation of the hip joint.
2. Muscle Weakness: In some cases, certain muscles around the hip joint may be weaker, resulting in poor support and stability. This weakness can contribute to dislocation or subluxation of the hip, where the ball of the hip joint partially comes out of its socket.
3. Abnormal Bone Development: In a growing child, the constant pressure and altered movement patterns may affect the development of the bones around the hip joint. Over time, this can lead to structural changes that further exacerbate hip problems.

Which children with cerebral palsy are most likely to have hip problems?
The children with most severe neurological damage (GMFCS level 4 and 5) are most likely to have hip problems in cerebral palsy. These children have severe grades of muscle spasticity, are non-ambulatory and have poor head, neck and trunk control.
What are the common Symptoms of Hip Problems in Cerebral Palsy?
Recognizing the signs of hip problems in individuals with cerebral palsy is essential for early intervention and improved outcomes.
Some of the common symptoms to watch out for include:
1. Hip Pain: Complaints of pain in the hip area, particularly during movement or weight-bearing activities, may indicate hip issues.
2. Limited Range of Motion: Reduced ability to move the hip joint fully may suggest tightness or contractures of the surrounding muscles.
3. Walking Abnormalities: An uneven or asymmetrical gait pattern, such as a limp or toe-walking, could be indicative of hip problems.
4. Difficulty Sitting or Standing: Children with hip problems may have difficulty sitting upright or standing without support due to instability or pain.
5. Visible Changes in Leg Length: Asymmetry in leg length or hip alignment may become apparent as the condition progresses.

What is the role of hip surveillance in preventing hip problems in children with Cerebral Palsy?
Hip surveillance is the process of early identification and monitoring of indicators of hip displacement in children with cerebral palsy. This involves periodic clinical and radiological evaluation of the hips in children with cerebral palsy. The periodicity of hip evaluation varies according the severity of neurological involvement. More severely affected and bed-ridden children should undergo hip evaluation more frequently than walking children.
What are the treatment Options for Hip Problems in Cerebral Palsy?
Early detection and intervention play a crucial role in managing hip problems in individuals with cerebral palsy. The treatment approach may vary based on the severity of the condition and the age of the individual.
Here are some common treatment options:
1.Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is an integral part of managing hip problems in cerebral palsy. It focuses on strengthening weak muscles, stretching tight muscles, and improving overall mobility.
2.Orthotics and Assistive Devices: Braces, splints, or orthotics may be prescribed to help support the hip joint, improve alignment, and enhance stability during walking.
3.Medications: In some cases, medications like muscle relaxants may be used to alleviate spasticity and muscle tightness around the hips.
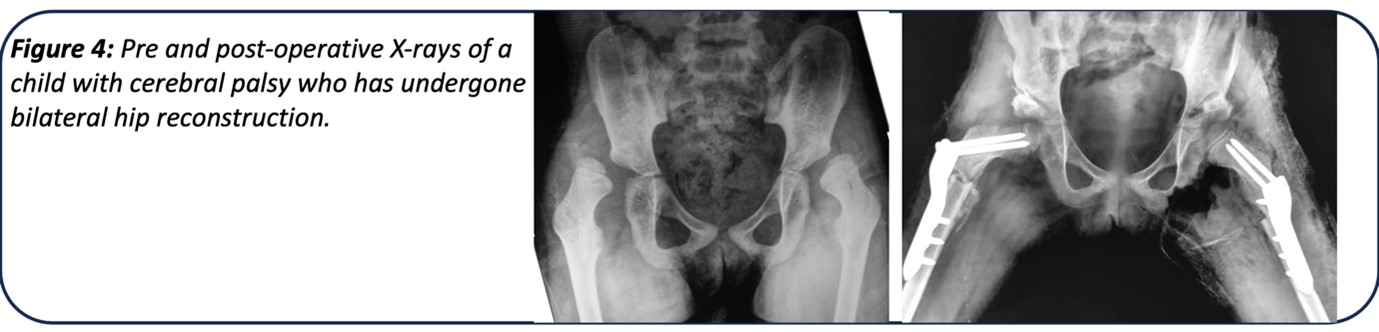
4.Surgical Intervention: Severe hip problems may require surgical intervention to correct deformities, stabilize the joint, or address hip dislocation.
5.Rehabilitation: Following surgery or any treatment, rehabilitation is essential to facilitate recovery and optimize function.
Conclusion:
Hip problems are common in individuals with cerebral palsy. Understanding the link between cerebral palsy and hip problems is crucial for early detection and intervention.
Timely treatment, including physical therapy, assistive devices, medications, and surgery when necessary, can significantly improve the quality of life for those with cerebral palsy and reduce the impact of hip problems on their mobility and daily activities.
A multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, caregivers, and the individual is key to ensuring the best possible outcomes for those with cerebral palsy and hip issues.


0 Comments